I. The Karnataka Co-operative Societies Act, 1959
The Karnataka Co-operative Societies Act, 1959 (Karnataka Act 11 of 1959) is the principal law governing co-operatives within the State. It provides the framework for registration, management, rights and liabilities of members, audit, inquiry, supersession, and dissolution of societies.


1. Objectives and Scope
Encourages economic and social betterment of people through self-help and mutual aid.
Applies to all co-operative societies registered in Karnataka, including agricultural, rural, urban, credit, housing, and producer co-operatives.
2. Registration of Co-operative Societies (Sections 4–9)
Minimum of ten members above 18 years required (or fewer for certain types).
Submission of application to the Registrar of Co-operative Societies with:
Memorandum of Association and Bye-laws
Proof of registered office and area of operation
Details of members and share capital
Registrar’s scrutiny of objectives, viability, and compliance before registration.
3. Bye-laws of a Society
Define membership conditions, share capital, powers, meeting procedures, duties of officers, dispute redressal, and profit allocation.
Amendment of bye-laws permitted with Registrar’s approval under Section 12.
4. Membership and Rights (Sections 16–20)
Membership open to individuals, firms, and other societies.
Rights include participation, voting, dividend, and nomination.
Disqualification for default or misconduct.
5. Management and Governance (Sections 27–30)
A Managing Committee or Board of Directors exercises executive powers.
Elections supervised by the Co-operative Election Commission.
Term of office, quorum, removal, and disqualification are prescribed by rules.
Responsibility to maintain records, minutes, and statutory registers.
6. General Body & Meetings
The General Body is the supreme authority of a co-operative.
Annual General Meetings (AGMs) are mandatory for presentation of audited accounts, budget, and statutory reports.
Failure to hold AGMs attracts penalties and suspension.
7. Capital, Funds, and Profits
Regulation of share capital, reserve funds, and borrowings.
Restriction on use of funds and investments.
Profit distribution limited to prescribed dividend percentages, ensuring cooperative character.
8. Accounts, Audit, and Inspection
Annual audit by a certified auditor or Co-operative Department auditor.
Power of Registrar to conduct inspection, inquiry, or special audit in case of mismanagement or complaints.
9. Disputes and Arbitration (Section 70)
Disputes between members, committees, or societies are referred to the Registrar of Co-operative Societies for adjudication or arbitration.
Appeals lie before the Co-operative Tribunal or High Court on points of law.
10. Supersession and Suspension (Section 30A–30C)
Registrar empowered to supersede or suspend a mismanaged committee.
Appointment of an Administrator or Interim Board to manage affairs.
11. Amalgamation, Division, and Dissolution
Voluntary or compulsory amalgamation/division by resolution and Registrar’s sanction.
Dissolution procedure includes settlement of assets and liabilities.
12. Offences and Penalties
Penalties for falsification of accounts, failure to file returns, or misuse of funds.
Civil and criminal liability of officers in case of fraud or breach of trust.
II. The Co-operative Societies (Amendment) Act, 2023
The Co-operative Societies (Amendment) Act, 2023 was enacted to modernize and democratize the co-operative sector across India, introducing reforms to improve transparency, digital governance, professional management, and regulatory efficiency.


1. Establishment of a Central Co-operative Election Authority
Independent statutory body to conduct free and fair elections for multi-state co-operatives and regulate state co-operative elections where applicable.
Ensures democratic governance and accountability of boards.
2. Enhanced Professional Management
Mandatory appointment of Chief Executive Officers (CEOs) and professionally qualified managers for efficient administration.
Introduction of performance standards, training, and evaluation norms.
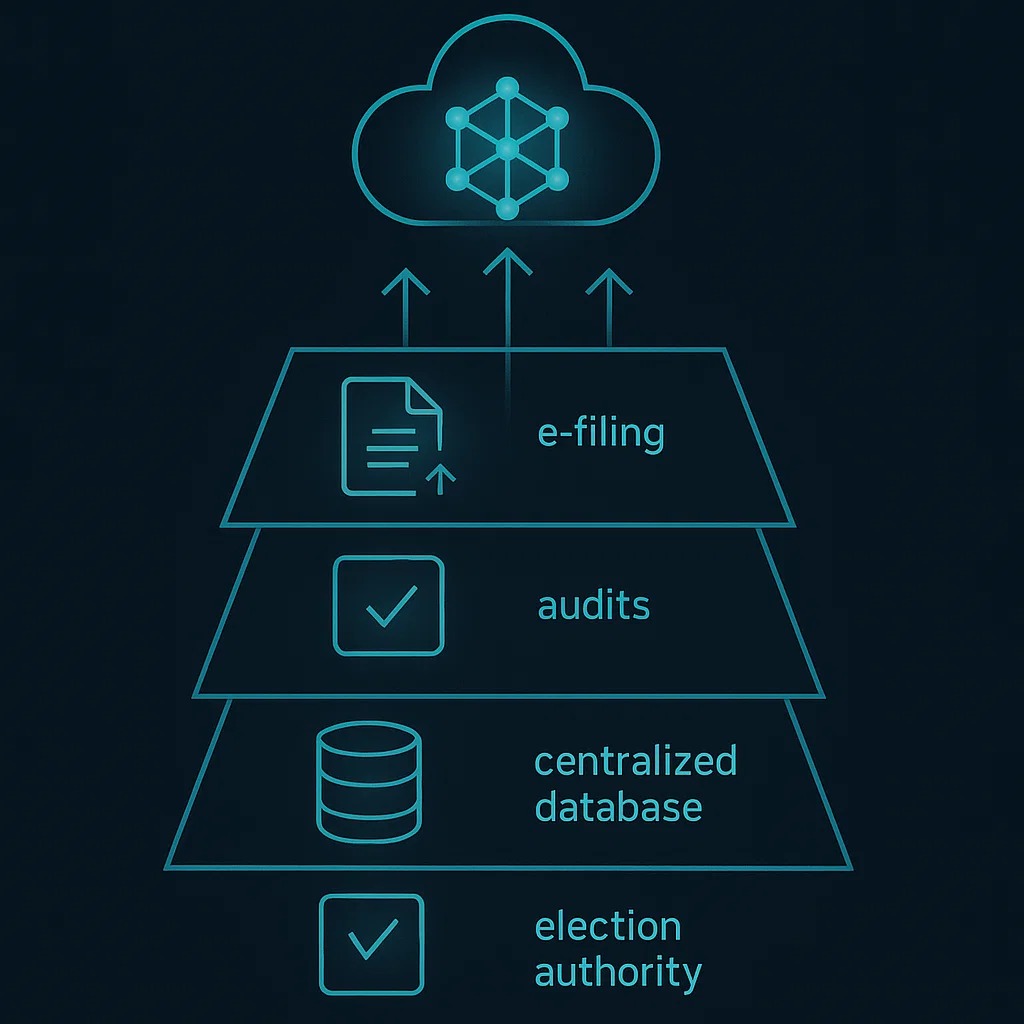
3. Digitization and E-Governance
Electronic filing of records, returns, and reports.
Creation of a Central Co-operative Database for transparency and accessibility.
4. Strengthened Member Participation
Increased protection of member rights and voting privileges.
Provisions for digital general body meetings, remote voting, and dispute mediation.
5. Financial Discipline and Audit Reforms
Compulsory statutory audit by empanelled auditors.
Strict timelines for submission of audit reports and annual statements.
Accountability mechanisms for fraudulent financial practices.
6. Inclusion and Gender Representation
Reservation of seats for women, SC/ST, and weaker sections in boards.
Promotes equitable participation in management.
7. Regulatory Oversight and Dispute Resolution
Creation of Co-operative Ombudsman for grievance redressal.
Expanded powers for inquiry and dissolution of defaulting societies.
Introduction of Alternate Dispute Resolution (ADR) mechanisms.
III. Our Exclusive Legal Services
At Legal Lifelines LLP, we provide specialized, sector-focused legal solutions for co-operative institutions under both the Karnataka Co-operative Societies Act, 1959 and the Co-operative Societies (Amendment) Act, 2023.


1. Formation and Registration
Drafting and vetting of Bye-laws, Memorandum of Association, and Charter Documents.
Advisory on type of co-operative — credit, agricultural, dairy, housing, producer, or service.
Representation before the Registrar of Co-operative Societies.
Obtaining Registration Certificate, PAN, and statutory licenses.
2. Governance, Elections, and Compliance
Assistance in election procedures and board management.
Legal audit of compliance with Registrar’s circulars and election notifications.
Conduct of annual meetings, filing of annual returns, and record maintenance.
3. Amendment, Restructuring, and Conversion
Drafting and filing of amendments to bye-laws, membership rules, or objectives.
Legal support in merger, division, or conversion of societies.
Transition advisory under 2023 reforms (digital governance, election rules, etc.).
4. Legal Representation and Dispute Resolution
Representation before:
Registrar of Co-operative Societies
Co-operative Tribunal
Civil Courts and High Court
Handling disputes regarding membership, elections, misappropriation, suspension, and recovery.
Arbitration and conciliation for inter-society disputes.
5. Inquiry, Audit, and Investigation
Support during Registrar’s inquiry, inspection, or suspension proceedings.
Defense against penal action or supersession of management.
Coordination with auditors and preparation of statutory compliance reports.
6. Dissolution and Liquidation
Legal assistance for voluntary or compulsory winding-up.
Settlement of accounts, liabilities, and distribution of surplus assets.
Representation during liquidation before competent authority.
7. Regulatory and Financial Advisory
Legal due diligence for funding, loans, and government subsidies.
Advisory on compliance under NABARD, RBI, and Registrar guidelines.
Structuring of co-operative federations and multi-state collaborations.
8. Training and Legal Awareness
Legal workshops for office bearers on statutory duties, elections, and compliance.
Advisory bulletins on new circulars and government notifications.
IV. Why Choose Legal Lifelines LLP


Exclusive Practice in co-operative and institutional laws.
Expert Representation before Co-operative Authorities and Tribunals.
Comprehensive Services from registration to dissolution.
Regulatory Insight into Karnataka and Central Co-operative reforms.
Transparent and Ethical Legal Guidance focused on compliance and sustainability.
V. Related Areas of Expertise


Society and Trust Formation under Karnataka Societies Act, 1960 and Trusts Act, 1882
Section 8 Companies under Companies Act, 2013
FCRA and Income Tax Exemptions (12A/80G) for co-operative and charitable entities
Public Authority Compliance under Right to Information Act, 2005
Legal Management and Institutional Restructuring
Conclusion
The co-operative sector continues to play a decisive role in empowering local economies and ensuring equitable growth. With the evolution of law through the Karnataka Co-operative Societies Act, 1959 and the Co-operative Societies (Amendment) Act, 2023, compliance, governance, and professional management have become indispensable. At Legal Lifelines LLP, we ensure that every co-operative institution — from rural credit societies to large housing federations — functions legally, transparently, and efficiently under the prevailing statutory framework.

